
Windows server user activity audit windows#
Privileged Access Management (PAM) solutions can address the native Windows privilege management gaps. As the annual Microsoft Vulnerabilities Reports have highlighted, removing admin rights and enforcing least privilege are perhaps the most powerful and effective way to reduce risk across Windows environments.

Use of privileged accounts, such as privileged Active Directory (AD) accounts by support staff, or local administrator rights by employees on workstations, increases the risk of compromise. While, every organization can expect to be breached at some point, prevention is always preferable to curing/remediation. How Endpoint Privilege Management Can Help If an application crashes, it could be that a hacker has tried to force a process to end to hide their actions. Event ID 4719 System audit policy was changed could also show malicious behavior. Event ID 104 Event Log was Cleared and event ID 1102 Audit Log was Cleared could indicate such activity.
Windows server user activity audit update#
Look for events like Scan failed, Malware detected, and Failed to update signatures. Another example is Windows Defender, which is included out-of-the-box in Windows Server 20. Application allow listing is worth enabling in audit mode to log processes and scripts that don’t normally run on your systems. For example, you might collect events that indicate a change in Windows Firewall configuration. Hackers usually start their penetration efforts on devices that users interactively log in to because they are more vulnerable.īelow, I’ve listed categories of events that you should consider monitoring. Start by prioritizing sensitive servers, like DCs, but don’t forget to audit and monitor workstations. For example, if you have a security policy that forbids domain administrators logging in to member servers, then any activity that indicates a breach of the policy should be logged and investigated.
In addition to Microsoft’s recommendations, consider auditing anything that might indicate unauthorized activity and that should involve an investigation. Alternatively, you can just configure the recommend audit settings. The templates contain many other security settings, not just audit policy, so you must test them thoroughly before deploying to production systems. The Security Compliance Toolkit contains templates for different server roles, like domain controller (DC) and member server, and they can be deployed using Group Policy. If you are not sure what to audit, Microsoft’s recommend audit settings in the baseline security templates for Windows Server are an ideal place to start.
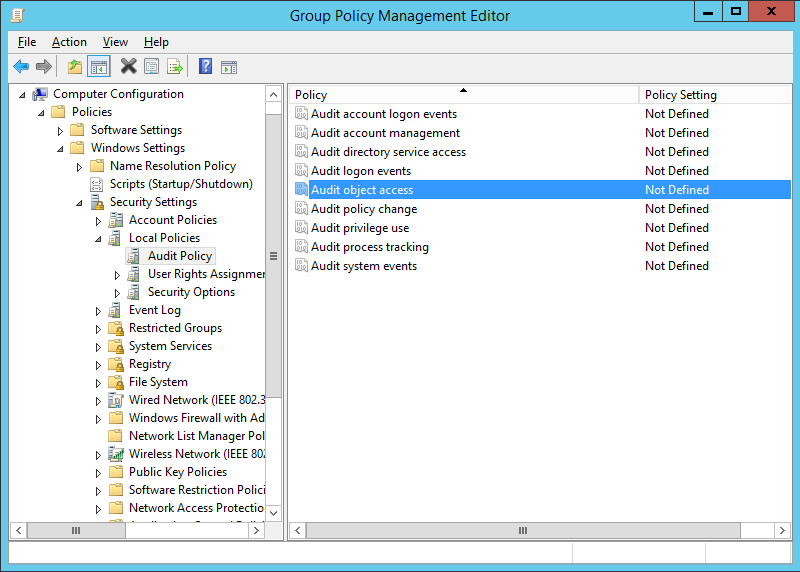
Legacy and advanced audit policy settings shouldn’t be used at the same time, so make sure you plan to retire legacy settings when switching to Advanced Policy Auditing. First introduced in Windows Server 2008, Advanced Audit Policy provides more granular control over Windows auditing so you can capture what’s important and eliminate noise. If you don’t have any audit policy configured, or if you are still using legacy audit settings, it’s time to set up Advanced Audit Policy. For example, your audit policy may determine that you want to log any remote access to a Windows machine, but that you do not need to audit login attempts from someone on your business premises. The Windows Audit Policy defines the specific events you want to log, and what particular behaviors are logged for each of these events. Windows Advanced Audit Policy and Security Baselines


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
